
A balance sheet serves as reference documents for investors and other stakeholders to get an idea of the financial health of an organization. It enables them to compare current assets and liabilities to determine the business’s liquidity, or calculate the rate at which the company generates returns. Comparing two or more balance sheets from different points in time can also show how a business has grown. Balance sheets are important for determining the financial health and position of your business at a certain point in time. When used with other financial statements and reports (such as your cash flow statement), it can be used to better understand the relationships between your accounts. As described at the start of this article, a balance sheet is prepared to disclose the financial position of the company at a particular point in time.
assets = liabilities + equity
You also have a business loan, which isn’t due for another 18 months. Get free guides, articles, tools and calculators to help you navigate the financial side of your business with ease. Liabilities are also separated into current and long-term categories. In other states, the program is sponsored by Community Federal Savings Bank, to which we’re a service provider.
Who prepares balance sheets?
Shareholders’ equity reflects how much a company has left after paying its liabilities. Assets are anything the company owns that holds some quantifiable value, which means that they could be liquidated and turned into cash. Balance sheets are useful tools for individual and institutional investors, as well as key stakeholders within an organization, as they show the general financial status of the company.
Balance Sheets Examine Risk
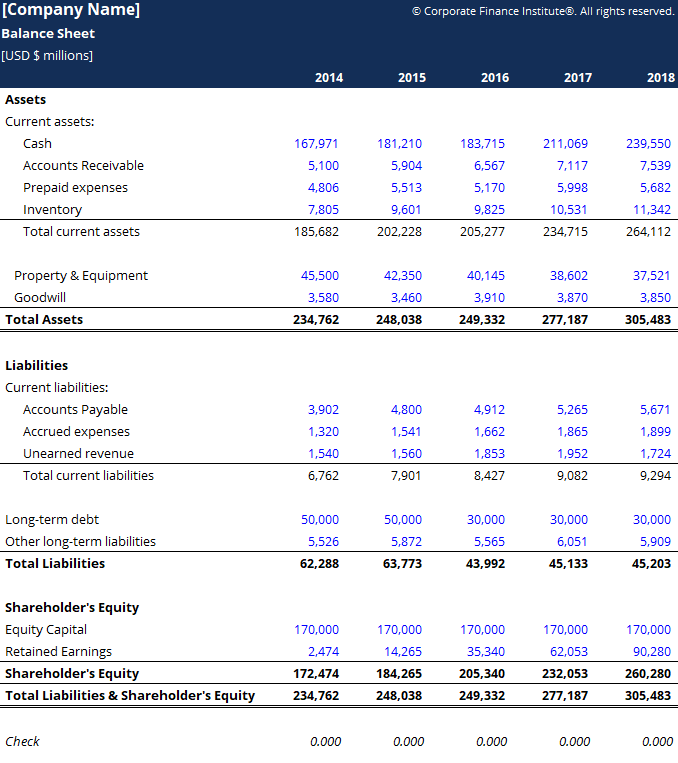
Calculating the Current Ratio (Current Assets ÷ Current Liabilities) and Quick Ratio (Cash and Receivables ÷ Current Liabilities) helps determine whether the company can meet its immediate obligations. For example, a high quick ratio may indicate a strong liquidity position, meaning the company can readily cover its liabilities without selling inventory, thus making it attractive for short-term creditors. By comparing your business’s current assets to its current liabilities, you’ll get a clearer picture of the liquidity of your company. In other words, it shows you how much cash you have readily available. It’s wise to have a buffer between your current assets and liabilities to at least cover your short-term financial obligations. The data from financial statements such as a balance sheet is essential for calculating your business’ liquidities.
A lot of times owners loan money to their companies instead of taking out a traditional bank loan. Investors and creditors want to see this type of debt differentiated from traditional debt that’s owed to third parties, so a third section is often added for owner’s debt. This simply lists the amount due to shareholders or officers of the company.
- Balance sheets are usually prepared by company owners or company bookkeepers.
- Assets refer to anything a business owns that offers current or future value.
- Public companies, on the other hand, are required to obtain external audits by public accountants, and must also ensure that their books are kept to a much higher standard.
- Looking under the surface of these figures lets analysts and investors see how the business is doing financially, and compare one company to another.
- Public companies are required to have a periodic financial statement available to the public.
- Investors and creditors generally look at the statement of financial position for insight as to how efficiently a company can use its resources and how effectively it can finance them.
After almost a decade of experience in public accounting, he created MyAccountingCourse.com to help people learn accounting & finance, pass the CPA exam, and start their career. It can be sold at a later date to raise cash or reserved to repel a hostile takeover. To measure the money remaining in the company's coffers after financing its activity. The resources are ordered according to whether or not they are due and payable. Detail of it could be found in the statement of change in equity and Noted to Financial Statements.
Unlike the income statement, the balance sheet does not report activities over a period of time. The balance sheet is essentially a picture a company’s recourses, debts, and ownership on a given day. This is why the balance sheet is sometimes considered less reliable or less telling of a company’s current financial performance than a profit and loss statement. Annual income statements look at performance over the course of 12 months, where as, the statement of financial position only focuses on the financial position of one day. The balance sheet, also called the statement of financial position, is the third general purpose financial statement prepared during the accounting cycle. It reports a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a single moment in time.
The balance sheet is basically a report version of the accounting equation also called the balance sheet equation where assets always equation liabilities plus shareholder’s equity. A company can use its balance sheet to craft internal decisions, though the information presented is usually not as helpful as an income statement. A company may look at its balance sheet to measure risk, make sure it has enough cash on hand, and evaluate how it wants to raise more capital (through debt or equity).
Companies typically select an ending period that corresponds to a time when their business activities have reached the lowest point in their annual cycle, which is referred to as their natural business year. While an asset is something a company owns, a liability is something it owes. Liabilities are financial and legal obligations to pay an amount of money to a debtor, which is why they’re typically tallied as negatives (-) in a balance sheet. Balance sheets are typically prepared at the end of set periods (e.g., annually, every quarter). Public companies are required to have a periodic financial statement available to the public.
If you were to take a clipboard and record everything you found in a company, you would end up with a list that looks remarkably like the left side of the balance sheet. Balance sheets are usually prepared by company owners or company bookkeepers. Internal or external accountants can also prepare and review balance sheets. If a company is public, public business development business plan accountants must look over balance sheets and perform external audits. With a firm understanding of the balance sheet basics, you can use this report to guide financial decision-making in your business. Although it takes time and effort to create an accurate balance sheet from scratch, it is a vital report you as a business owner should have.

